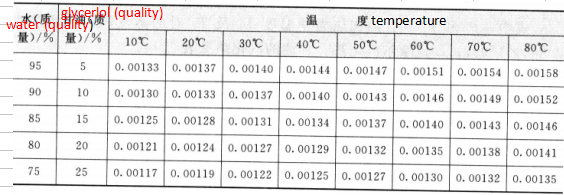
/(cal/(g.0C))
1. Estimated freezing point and the maximum specific heat capacity of the mixture at the time of the component.
2. The minimum value of specific heat capacity at the same concentration.
The optimum concentration of the glycerol-water solution as the refrigerant in a certain temperature range can be selected by using Table 2.10. For example, when the temperature of the freezing liquid is 29 ° C, the concentration of 55% is selected [its specific heat capacity is 1.6 cal / (g ° ° C), the heat buffering efficiency is the best], and when the temperature of the freezing liquid is 18 -* C, the selection is made. 40% concentration.
A specific solution of glycerol dissolved in a solvent, the specific heat capacity of the solvent and the specific heat capacity of glycerol are calculated as follows:
(M+ m)S=sM+s’ m
where M is the mass of the solvent;
- Specific heat capacity of S-solution;
M-The quality of glycerol
s-The specific heat capacity of the solvent;
s’-Specific heat capacity of glycerol in solution
3. Freezing point
The freezing point of pure glycerin is 18.17C, but this glycerol which exists in a crystalline state is rare.
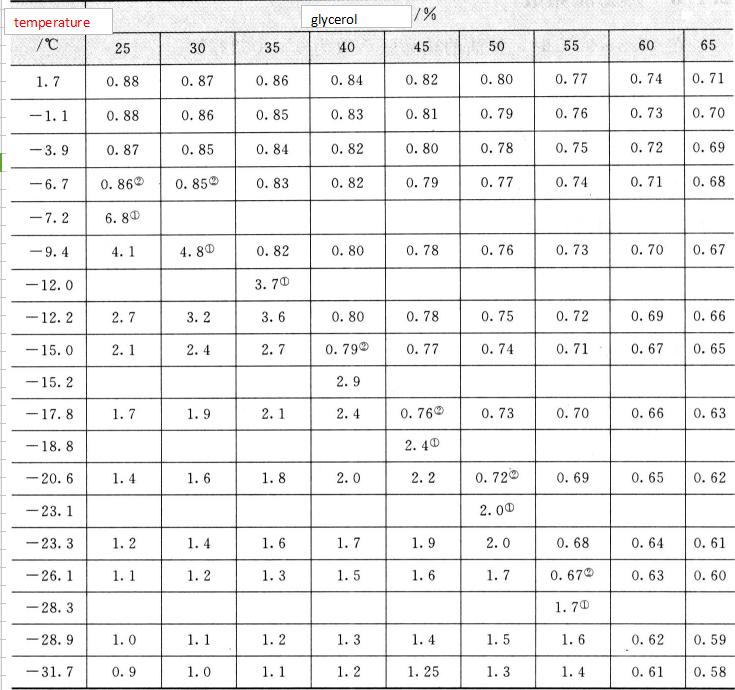
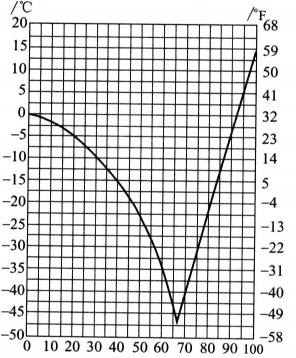
Therefore, some people mistakenly believe that glycerin has a quality problem. In fact, there is no problem in using this glycerin after heating. The reason why it is rare is that glycerin often contains water, which causes a tendency to be too cold, thus lowering the freezing point of glycerin. When the glycerol concentration was 66.7% (molar ratio was about 1:2.5), a eutectic mixture was formed, and the freezing point dropped the most, to be 43.5C. Figure 2.5 shows the relationship between glycerol concentration and freezing point. Glycerin is mixed with volatile antifreeze agents such as methanol and ethanol and can be used in automotive engines. Glycerol can reduce the volatility of alcohol to prevent freezing after the alcohol evaporates, causing damage to the machine. Glycerol-water solutions can be used in refrigeration technology and can also be used in the food industry. Because glycerin is non-toxic, it can be eaten and is widely used.
Glycerol (quality)/%
Figure 2.5 Relationship between glycerol concentration and freezing point
4.Thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of glycerol increases as the water content increases, and in addition, rises as the temperature rises.
And it is a straight line change. The thermal conductivity of glycerol is 0. 000691 cal / (cm. s. C), glassy
The glycerol is 0. 0007601X10- 6cal/(cm.s. °C) at 78.5 °C.
The thermal conductivity of glycerin and glycerol aqueous solutions is shown in Table 2.13.
Table 2.13
Sheet 2.13 Thermal conductivity of glycerin and glycerol aqueous solution / [cal / (cm. s. C)]