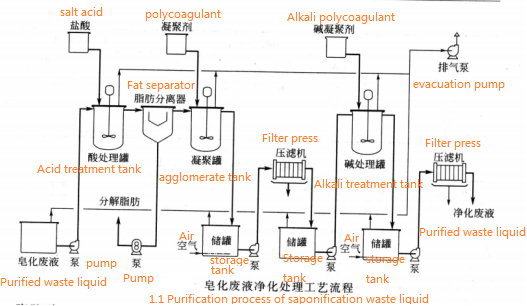
The general composition of saponification waste liquor is about 80% water, 10% – 15% inorganic salt (NaCI), 6% – 10% glycerol, 0.1% – 1.0% fatty acid salt (Na salt), 0.1% – 0.5% NaOH. They are from nitrogenous compounds (proteins), phospholipids and resins, pigments, glycerol fermentation products such as propylene glycol (about 0.1% – 0.5%) etc. In the process of soap boiling, the content of fatty acid salts in the saponification waste liquor will increase greatly because of the insufficient salt concentration or the high free alkali in the waste liquor. It is noteworthy that the saponification waste liquor, especially the dilute glycerol recovered from the inferior oil, will produce fermentation phenomenon if the storage time is too long or the storage environment is unclean. Besides affecting the yield of glycerol, it will also affect the operation and control of the refining process (filtration, concentration of clear water and distillation of crude glycerol) and the quality of the product. Therefore, we should take seriously the purification operation of saponification waste liquid. The treatment of saponification waste liquid is divided into two parts: acid treatment and alkali treatment. The purification process of saponification waste liquor is shown in Figure 1.1.
1.1Acid treatment (including acid decomposition and acid decomposition of fatty acids)
The purpose of the acid treatment operation is to neutralize the free alkali in the saponification waste liquor and to decompose fatty acid salts to produce fatty acids.
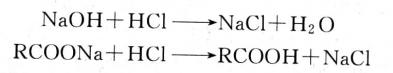
Fatty acids and flocculants, such as ferric chloride, precipitate fatty acids to form metal salts:
![]()
In the acid treatment of saponification waste liquid, as flocculant, ferric chloride mainly has the following functions:
Formation of iron soap precipitation:
![]()
Isoelectric point coagulation: In addition to fatty acid salts, saponification waste liquor also contains amino acids, proteins, nitrides and other sodium salts, they are amphoteric compounds. They can form salts with acids and bases. The hydrolysis of ferric chloride is generated by hydrochloric acid.
![]()
Therefore, ferric chloride can change the Ph value of saponification waste liquid. Neutral dipole ions exist when Ph reaches a certain value. At this time, the solubility in water is the smallest, and this Ph value is isoelectric point of the substance. Adjusting the Ph value to the isoelectric point (if the colloid isoelectric point is Ph 5.2; the protein is Ph 4.6-4.9; the amino acid isoelectric point is Ph 2.9), such substances can be precipitated from the solution.
Electroneutralization: The impurities precipitated from acidic saponification waste liquor are in colloidal state. These impurities are negatively charged and can not agglomerate into large particles because of mutual repulsion. After adding ferric chloride, the iron ions are neutralized with the negatively charged impurities colloids, resulting in precipitation.
Adsorption: The atoms on the solid surface have certain surface energy and tend to adsorb some substances to reduce the surface energy. Iron soap and excess iron ions and alkali to form iron hydroxide are huge precipitates, with a large surface area, can adsorb a large number of impurities.
Several functions of ferric chloride are interrelated, interacting and restricting each other. Therefore, we must strictly control and strictly operate.
Saponification waste liquor is alkaline. First, HCI and H2SO4 are used to neutralize, neutral fat is skimmed, HCI or H2SO4 is added to PH3.5-4 under compressed air agitation, and black fat is still skimmed out (fatty acids and other impurities produced by acidification and decomposition of fatty acid salts are named because they are black, and black fatty acids can be treated to recover fatty acids).
Under the stirring of the compressed air, add FeCL3 solution (concentration is generally 38%) to PH3.5-4.2, continue to turn, 10 MIN after sampling and filtering, 10 ML filtrate added 2 drops of 5% FeCL3 solution, shake well, after 5 minutes should be no turbidity, if there is turbidity, then add FeCL3 solution and continue to test, must make the solution clear and transparent. However, if the Ph value is too low, the fatty acid iron salt will be dissolved and the treatment effect will be reduced. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out alkaline recovery operation (especially to treat the saponification waste liquor of low-grade oil and grease should be particularly careful, otherwise it will affect the filtration).

