Because of the different process of splitting decomposition, the concentration and impurities of glycerol in sweet water differ greatly with catalysts hydrolyzed at low temperature and atmospheric pressure, medium temperature and pressure, and without catalysts hydrolyzed at medium pressure and high pressure, so the purification methods are also different. The following two parts are introduced:
- Purification of Sweet Water without Catalyst
The quality of sweet water without splitting decomposition of oil depends on the quality of the oil. After degumming and alkali refining, there are few impurities in the sweet water after pyrolysis, and the concentration of glycerol is between 10% and 25%. The purification method is also simple.
Purification operation method: Now the sweet water is heated to about 70 degrees Celsius, static settlement as far as possible, the upper layer of fat is skimmed out. If the sweet water is opaque (especially in medium temperature and medium pressure hydrolysis operation, when the hydrolysis depth is low, or when the high pressure hydrolysis interface is controlled low), it shows that there are more incomplete hydrolysis of fat mixed, inorganic acid or salt can be added a little to destroy its emulsification. Separation of fat. Otherwise, the effect of sweet water treatment is not good, which not only affects the evaporation of purified water, but also makes the filtration difficult.
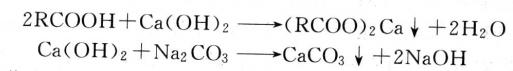
At 60-70℃, Na2CO3 solution was added to the compressed air, and the PH value was controlled at about 9. CaCO3 precipitation was formed and precipitated. The purified water was purified after filtration.
When refined glycerol is not produced by distillation, the second clean water can be decolorized by activated carbon adsorption, and then purified by ion exchange resin to obtain pure purified sweet water. The refined glycerol with more than 98% glycerol content can be obtained by direct evaporation and concentration of purified sweet water treated by ion exchange resin.
Compared with distilled glycerol, refined glycerol without distillation has poor thermal stability and colour, but the recovery of glycerol is greatly improved. It is necessary to study carefully whether the low quality sweet water with more impurities is treated with ion exchange resin.
Protein and other impurities in sweet water are easy to ferment and deteriorate. They are not suitable for long-term storage. Sweet water should be purified and treated in time. In order to reduce glycerol loss, the sweet water container can be cleaned regularly.
Aluminum salts have a good effect on fatty acid treatment, and the adsorptive effect of the formed fatty acid aluminium salts is also good. Aluminum salts are mostly used abroad to treat fatty substances in sweet water, and quicklime is mostly used in China. If conditions permit, aluminium salts are also worth considering.

